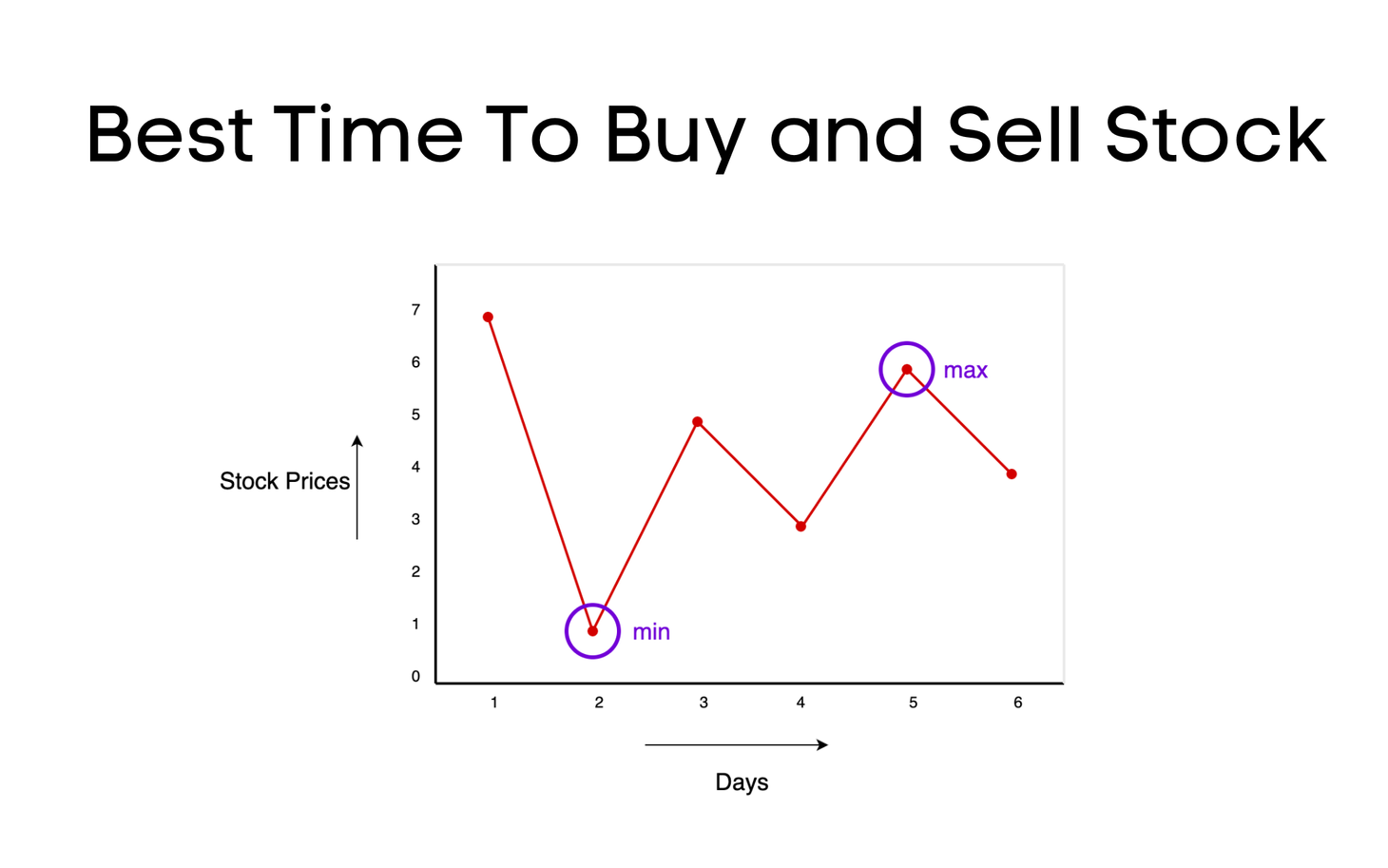
Bitwise OR, Computations, and Examples
A Bitwise OR is a binary operator that takes two-bit patterns of equal length and performs the logical inclusive OR operation on each corresponding bits pair. The result in each position is 0 if both bits are 0. Otherwise, the result is 1.