Difference Between String and char[] in Java
Table of Contents
Short answer
Strings
String is an object with many helpful methods. String class in Java's standard library is designed to handle text as a sequence of characters.
A string of characters (string object) is non-modifiable or immutable in Java. Once you've created it, you cannot modify it. This means when you perform operations on a string, you always get a new string, creating a new object in memory. Million operations - million new objects. StringBuilder with its append method optimizes this.
char[] (array of characters)
char[] is an array of characters with only methods from objects, which are mostly not helpful.
The size of an array is fixed. Once created, you cannot increase the array size but replace one array item with another.
More detailed answer
Strings
String has no primitives, it is a defined class type and has methods to operate on it.
A String is a -
- Sequence of characters. ✅
- Array/list of characters. ✅
- Group/set of characters? ❌ (this is not true).
Create, access, and other methods
Strings can be created in Java using string literals or by creating a String object using new keyword.
// creating a string object
String name = new String("John Doe");
// using string literal
String name = "John Doe";
// length
name.length();
// concatenation: Strings can be concatenated using the + operator or by using the concat() method.
String str1 = "Hello";
String str2 = "World";
String result = str1 + " " + str2; // "Hello World"
// accessing/iterating over each character in string
for(int i = 0; i < name.length(); i += 1) {
char ch = name.charAt(i);
System.out.println(ch);
}
for(char ch: name.toCharArray) {
System.out.println(ch);
}String comparison
"str1" == "str2" // double equals here compares references in memory
// Instead use equals or equalsIgnoreCase
"str1".equals("str2");
"str1".equalsIgnoreCase("str2");"abc" == "abc" returns true. That's because of the Java string pool, the special memory region where the JVM stores strings. Java tries to optimize memory that way and refers identical strings to the same place in memory.
String pool
Java maintains a special memory area called the "String Pool" for string literals. This can help conserve memory by reusing common strings.
char[]
char[] in Java stores an ordered sequence of characters. char[] arrays are mutable, meaning you can change the value of individual characters after the array is created.
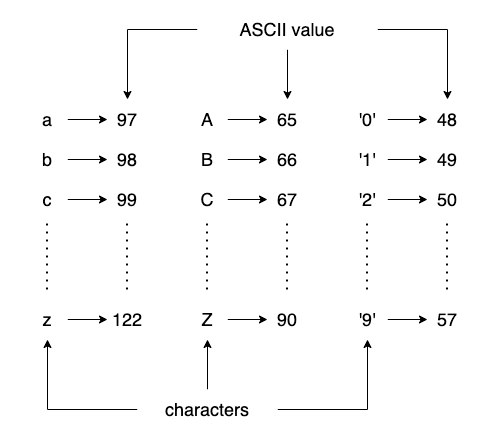
ASCII values
ASCII values are in between [0 255]. We have 256 unique characters in ASCII, each occupying 8-bit OR 1-byte memory.
Create, access, and other methods
// declaration
char[] charArray;
// declaration and initialization
char[] charArray = {'H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o'};
// access elements
char firstChar = charArray[0]; // This will be 'H'
// length
int length = charArray.length; // This will be 5
// iterate
for(char ch : charArray) {
System.out.print(ch + " "); // This will print: H e l l o
}
// modifying
charArray[0] = 'h'; // Changes the first element to 'h'
char[] arrays are commonly used for situations where mutable character data is needed, such as when performing low-level text processing.
String to char[] conversion
You can convert a String to a char[] using the toCharArray() method of the String class.
String str = "Hello";
// Converts the string to a char array
char[] charArray = str.toCharArray(); // ['H', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o']Gopi Gorantala Newsletter
Join the newsletter to receive the latest updates in your inbox.