What Are Primitive Data Types In Java?
Table of Contents
Introduction
Data types in Java are divided into two types that are used to define variables include:
- Primitive data types
- Non-primitive (or reference) data types.
Sketch
The following sketch helps you understand how everything is divided based on its type.
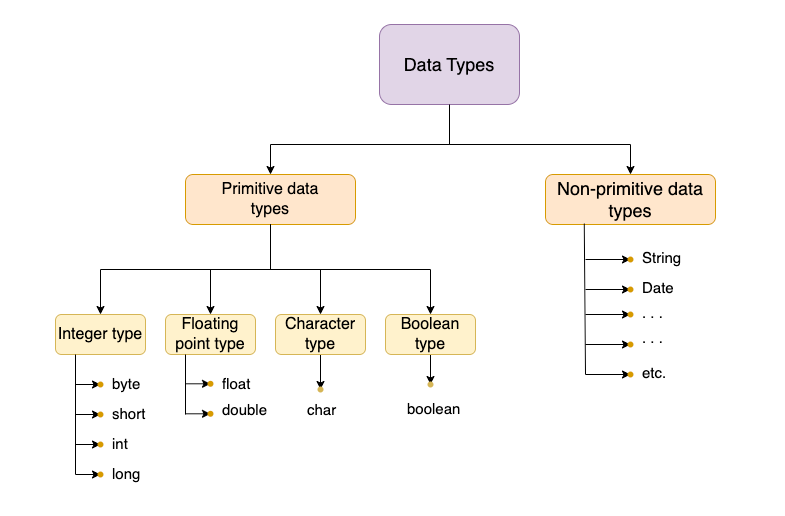
Primitive data types
In Java, most of the work is done by primitives. These primitive data types are the foundation of all other types.
- They are used to store simple values such as numbers and characters.
- They are stored directly in memory and are accessed faster than non-primitive data types.
There are eight primitive data types in Java: byte, short, int, long, float, double, char and boolean.
The size and range of values that can be stored in a primitive data type depending on the type itself. For example, a boolean can only hold the values true or false, while a long can hold values from -263 to 263-1.
Hence, the 8 primitive data types in Java are categorized into 4 types.
- Integer types -
byte,short,int, andlong. - Floating point types -
floatanddouble. - Character type -
char. - Boolean type -
boolean.
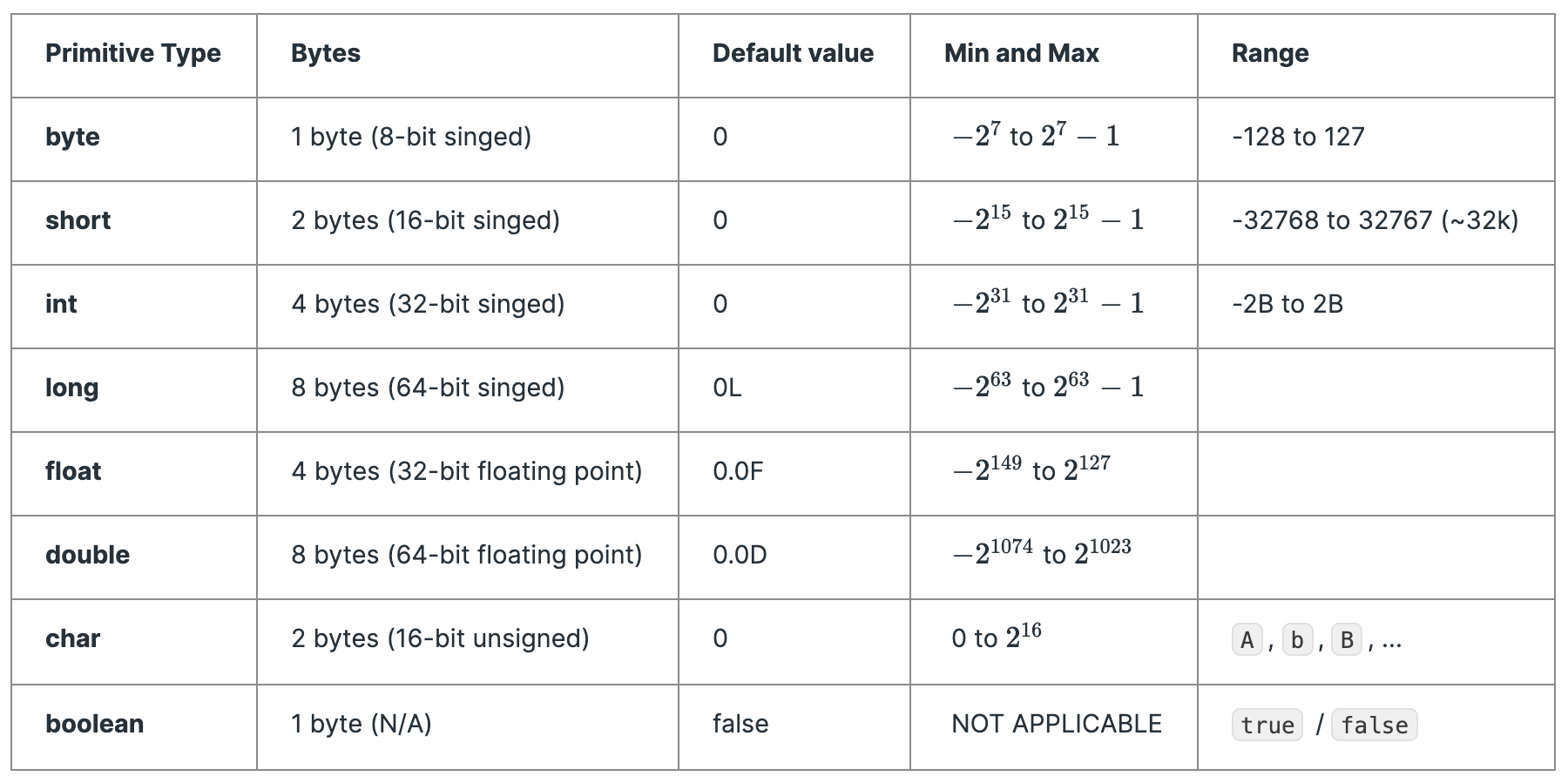
Tabular chart
Let us see the bytes size, default value, min and max and ranges of all the primitive data types.
Integer types - (byte, short, int, and long)
There are 4 data types, that store numeric data in programs. They are:
byte:
A byte is an 8-bit signed integer.
- Occupies
1byte. - The default value is
0. - It can store a min value of
-2^7or-128and a maximum value of(2^7 - 1)or127.
public class ByteType {
public static void main(String[] args) {
byte A = -1;
byte B = 20;
byte C = 3;
byte add = (byte) (B + C);
byte subtract = (byte) (B - C);
System.out.println(add); // 23
System.out.println(subtract); // 17
}
}The maximum and minimum values of byte can be found at:
byte high = Byte.MAX_VALUE; // high == 127
byte low = Byte.MIN_VALUE; // low == -128short:
A short is a 16-bit signed integer.
- Occupies
2bytes. - The default value is
0. - It can store a min value of
-2^15or-32768and a maximum value of(2^15 - 1)or32767.
public class ShortType {
public static void main(String[] args) {
short A = -48;
short B = 987;
short C = 17;
short add = (short) (B + C);
short subtract = (short) (B - C);
System.out.println(add); // 1004
System.out.println(subtract); // 970
}
}The maximum and minimum values of short can be found at:
short high = Short.MAX_VALUE; // high == 32767
short low = Short.MIN_VALUE; // low = -32768int:
This is one of Java's most used data types, storing 4 bytes of data. According to Java API, the Integer class wraps a value of the primitive type int in an object.
An int is a 32-bit signed integer.
- Occupies
4bytes. - The default value is
0. - It can store a min value of
-2^31or-2Band a maximum value of(2^31 - 1)or2B.
public class IntType {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int A = -48;
int B = 987;
int C = 17;
int add = B + C;
int subtract = B - C;
System.out.println(add); // 1004
System.out.println(subtract); // 970
}
}
The maximum and minimum values of short can be found at:
int max = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // -2147483648
int min = Integer.MIN_VALUE; // 2147483647long:
By default, long is a signed integer (In Java 8, it can be either signed/unsigned).
Signed: It can store a minimum of 2^63 and a maximum of (2^63 - 1).
Unsigned: It can store a minimum value of 0 and a maximum value of (2^64 - 1).
- Occupies
8bytes. - The default value is
0L.
If you assign long A = 100, Java assumes it as a int type. Appending L makes it a long.
public class LongType {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long A = -42;
long B = 284;
long C = 73;
long bigNumber = 549755813888L;
long addedLongs = B + C; // 284 + 73 = 357
long subtractedLongs = B - C; // 284 - 73 = 211
System.out.println(addedLongs); // 357
System.out.println(subtractedLongs); // 211
}
}
The maximum and minimum values of long can be found at:
// Max and Min
long high = Long.MAX_VALUE; // high == 9223372036854775807L
long low = Long.MIN_VALUE; // low == -9223372036854775808LNote: LetterLappended at the end of thelongliteral is case insensitive, however it is good practice to use capital as it is easier to distinct from digit one.
2L == 2l // trueFloating types - (float, double)
float:
A float is a single-precision 32-bit floating point number.
- Occupies
4bytes. - The default value is `0.0F`.
- It can store a min value of
-2^149and a maximum value of2^127.
By default, decimals are interpreted as doubles. To create a float, append an f to the decimal literal.
A float is precise to roughly an error of 1 in 10 million.
Float.POSITIVE_INFINITY
Float.NEGATIVE_INFINITY
Float.NaNNaN stands for the results of an operation that cannot be determined. Such as dividing two infinite values.
public class FloatType {
public static void main(String[] args) {
float f1 = 0f;
float f2 = -0f;
System.out.println(f1 == f2); // true
System.out.println(1f / f1); // Infinity
System.out.println(1f / f2); // -Infinity
System.out.println(Float.POSITIVE_INFINITY / Float.POSITIVE_INFINITY); // NaN
}
}
0f and -0f are different but == yields true.
public class FloatType {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// addition
float add = 37.2f + -2.6f; // result: 34.6
System.out.println(add);
// subtraction
float subtract = 45.1f - 10.3f; // result: 34.8
System.out.println(subtract);
// multiplication
float multiply = 26.3f * 1.7f; // result: 44.71
System.out.println(multiply);
// division
float division = 37.1f / 4.8f; // result: 7.729166
System.out.println(division);
// modulus
float modulus = 37.1f % 4.8f; // result: 3.4999971
System.out.println(modulus);
}
}double:
A double is a double-precision 64-bit floating point number.
- Occupies
8bytes. - The default value is `0.0D`.
- It can store a min value of
-2^1074and a maximum value of2^1023.
public class DoubleType {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double d1 = 0d;
double d2 = -0d;
System.out.println(d1 == d2); // true
System.out.println(1d / d1); // Infinity
System.out.println(1d / d2); // -Infinity
System.out.println(Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY / Double.POSITIVE_INFINITY); // NaN
}
}public class DoubleType {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double A = -7162.37;
double B = 974.21;
double C = 658.7;
double addedDoubles = B + C; // 315.51
double subtractedDoubles = B - C; // 1632.91
double scientificNotationDouble = 1.2e-3; // 0.0012
}
}Character type - (char)
char:
A char can store a single 16-bit Unicode character. A character literal is enclosed in single quotes.
- Occupies
2bytes. - The default value is
0. - It can store a minimum value of
\u0000(0in the decimal representation, also called thenullcharacter) and the maximum of\uffffor(2^16 - 1). - The char values are
A,B,a,d, etc.
public class CharType {
public static void main(String[] args) {
char myChar = 'u'; // 'u'
char myChar2 = '5'; // '5'
char myChar3 = 65; // 'A'
}
}
Boolean type - (boolean)
boolean:
A boolean can store one of two values, either true or false.
- Occupies
1bytes. - The default value is
false. - There is no min or max for
booleandata type.
public class BooleanType {
public static void main(String[] args) {
boolean a = true; // true
boolean b = false; // false
boolean notA = !a; // false
boolean notB = !b; // true
boolean aAndB = a && b; // false
boolean aOrB = a || b; // true
boolean aXorB =a ^ b; // true
}
}
Characteristics of Primitive Types
Primitive types in Java share several key characteristics that distinguish them from reference types (like objects and arrays):
Fixed Size
Each primitive type has a predetermined size in memory, which ensures predictable memory usage. Here's a quick overview
Stored by Value
Primitive types store their actual values directly in memory. For example, when you assign a value to an int, the memory location holds that specific integer value.
int age = 25; // The memory location for 'age' holds the value 25 directly.
No Methods or Properties
Unlike objects, primitive types do not have methods or properties. They are simple and straightforward, designed to hold basic data without additional functionality.
Faster Performance
Accessing and manipulating primitive types is generally faster than working with objects because they are simple and stored directly in memory without the overhead associated with object references.
Default Values
Each primitive type has a default value assigned when declared as a class member but not initialized:
| Primitive Type | Default Value |
|---|---|
byte, short, int, long | 0 |
float, double | 0.0 |
char | '\u0000' (null character) |
boolean | false |
Gopi Gorantala Newsletter
Join the newsletter to receive the latest updates in your inbox.
