What Are Functional Interfaces in Java? With Examples
This is the introductory lesson on functional interfaces. Introduced in Java SE 8, these are powerful and most useful as either lambdas or method reference can use it.
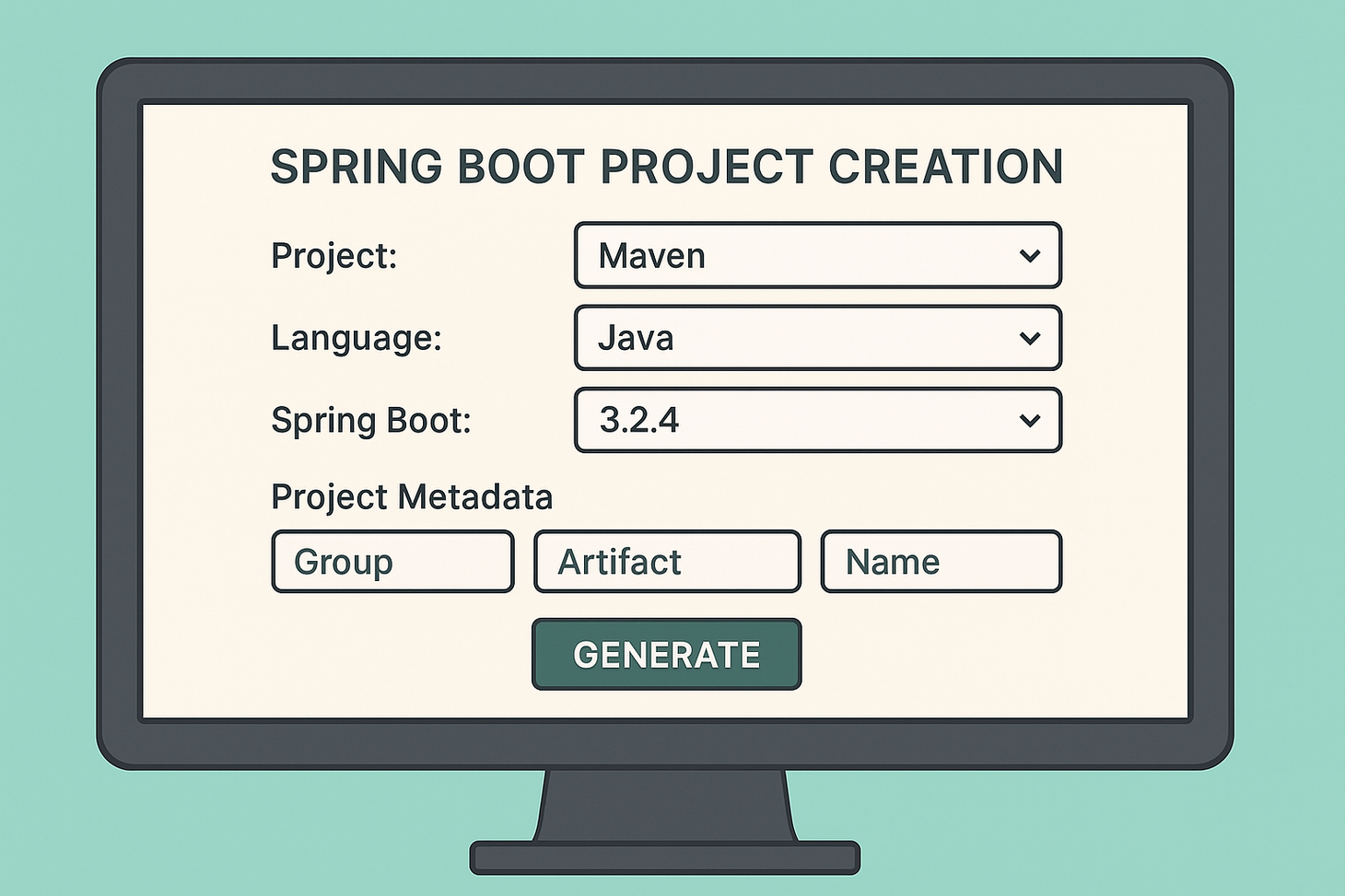
Learn how to create a Hello World Spring Boot application using Lombok for cleaner code and the H2 in-memory database for rapid development. This step-by-step guide includes annotations, project setup, REST API, H2 console access, and more to kickstart your Spring Boot journey.
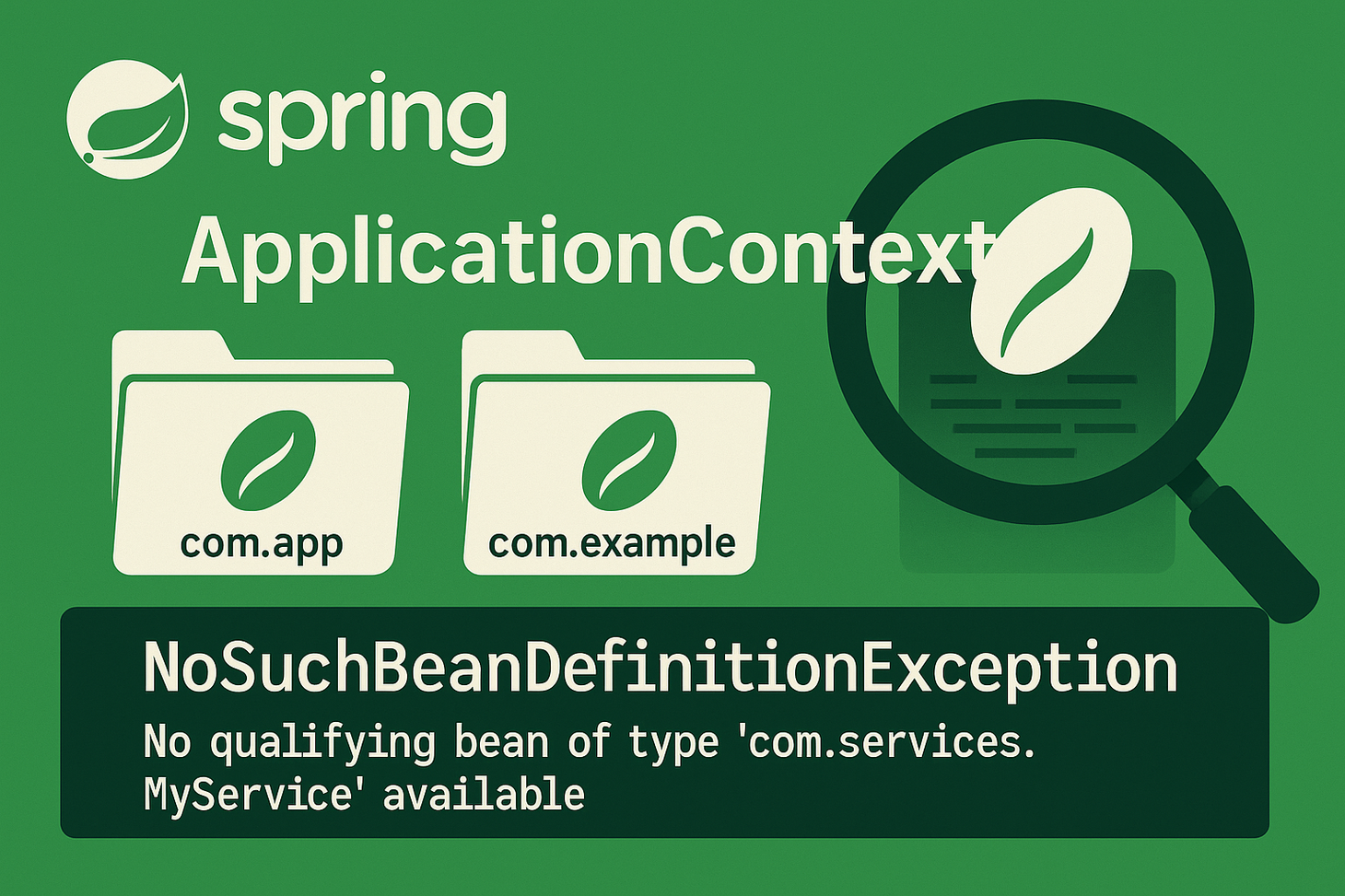
Learn how to fix NoSuchBeanDefinitionException in Spring Boot with clear examples and best practices for dependency injection, package scanning, and bean registration.
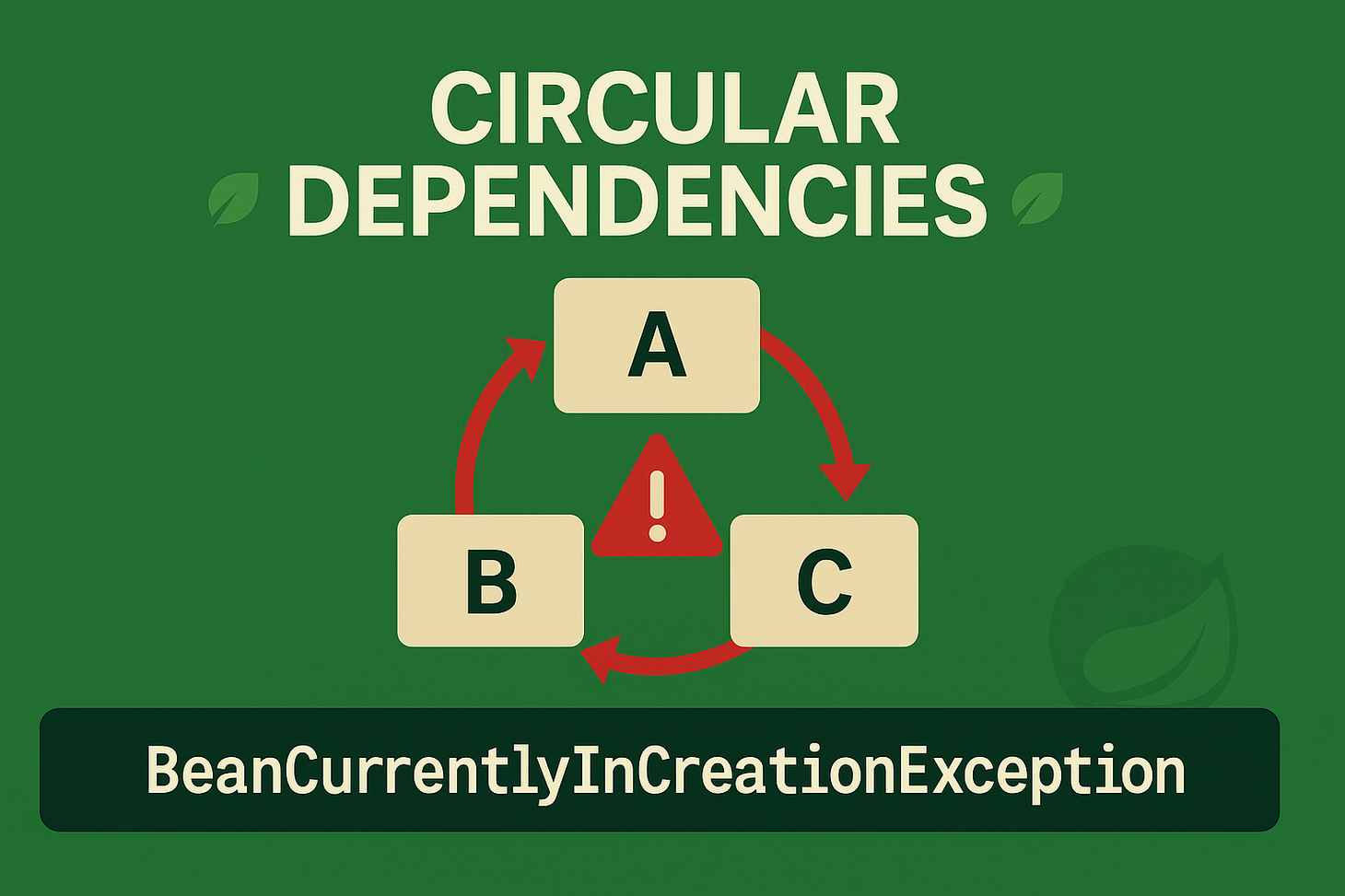
Spring Boot’s DI can backfire with the dreaded BeanCurrentlyInCreationException, signaling an unresolvable circular dependency. Learn why cycles occur, how they breach SOLID principles, and three fixes—refactor to break loops, use @Lazy injection, and static @Bean factory methods—to restore startup.