Mastering Spring Boot: Building Production-Ready Microservices
Spring Boot has revolutionized Java application development by eliminating boilerplate configuration and providing a streamlined approach to building production-ready applications. In this comprehensive guide, we'll explore advanced Spring Boot concepts and patterns that will help you build robust, scalable microservices that can handle real-world demands.
Understanding Spring Boot's Architecture
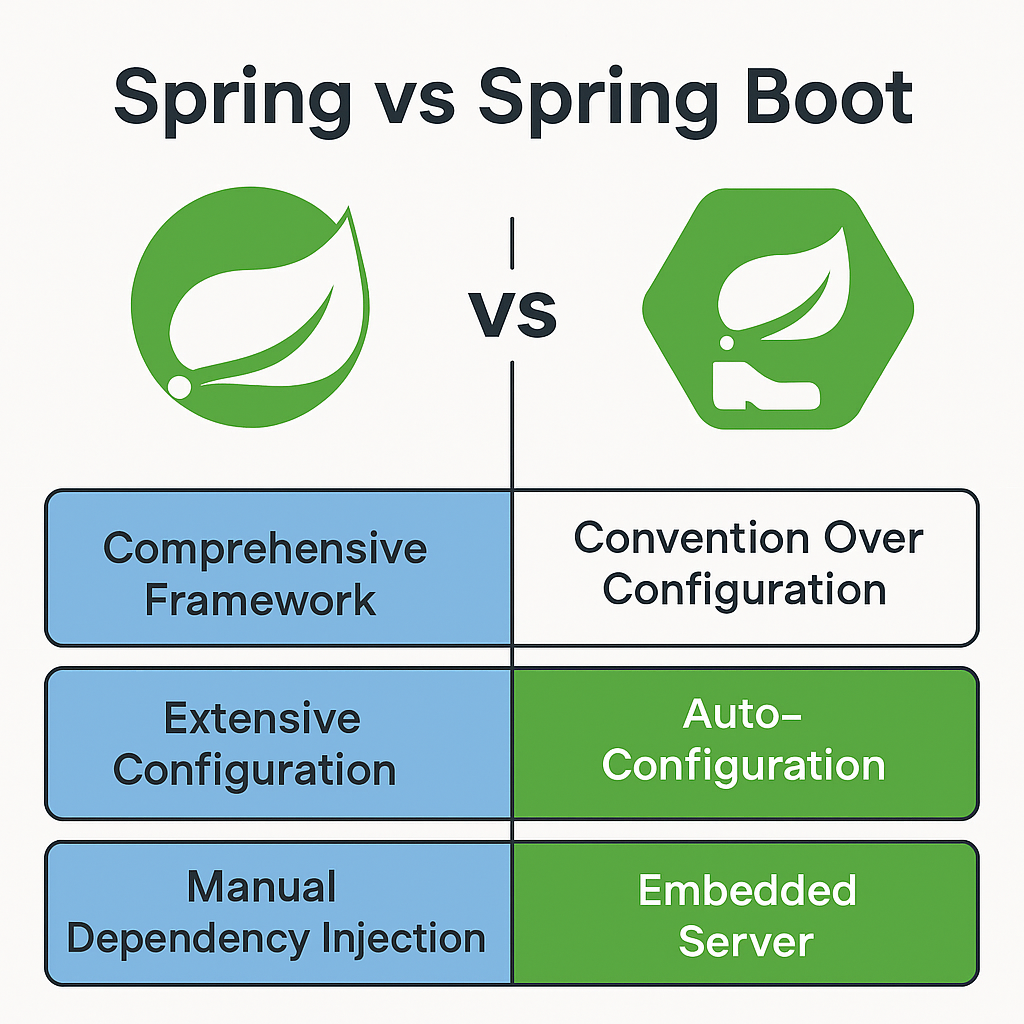
Spring Boot's power lies in its opinionated defaults and auto-configuration capabilities. When you start a Spring Boot application, it automatically configures your application based on the dependencies you've added to your classpath. This convention-over-configuration approach dramatically reduces development time while maintaining flexibility.
Auto-Configuration Magic: Spring Boot scans your classpath and automatically configures beans based on what it finds. For instance, if it detects H2 database on the classpath, it automatically configures an in-memory database. If it finds Spring MVC, it sets up a DispatcherServlet. This intelligent behavior is powered by @EnableAutoConfiguration and conditional annotations.
Embedded Server Architecture: Unlike traditional Java web applications that require external application servers, Spring Boot embeds Tomcat, Jetty, or Undertow directly into your application. This creates a self-contained executable JAR that simplifies deployment and scaling.
Building a Robust REST API
Let's dive into creating a production-ready REST API with proper error handling, validation, and documentation:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api/v1/products")
@Validated
@Slf4j
public class ProductController {
private final ProductService productService;
private final ProductMapper mapper;
@GetMapping
public ResponseEntity<Page<ProductDTO>> getAllProducts(
@PageableDefault(size = 20, sort = "createdAt,desc") Pageable pageable,
@RequestParam(required = false) String category,
@RequestParam(required = false) BigDecimal minPrice,
@RequestParam(required = false) BigDecimal maxPrice) {
Specification<Product> spec = Specification.where(null);
if (StringUtils.hasText(category)) {
spec = spec.and(ProductSpecifications.hasCategory(category));
}
if (minPrice != null) {
spec = spec.and(ProductSpecifications.priceGreaterThan(minPrice));
}
if (maxPrice != null) {
spec = spec.and(ProductSpecifications.priceLessThan(maxPrice));
}
Page<Product> products = productService.findAll(spec, pageable);
Page<ProductDTO> productDTOs = products.map(mapper::toDTO);
return ResponseEntity.ok()
.header("X-Total-Count", String.valueOf(products.getTotalElements()))
.body(productDTOs);
}
@PostMapping
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CREATED)
public ProductDTO createProduct(@Valid @RequestBody CreateProductRequest request) {
log.info("Creating new product: {}", request.getName());
Product product = mapper.toEntity(request);
Product savedProduct = productService.save(product);
return mapper.toDTO(savedProduct);
}
@PutMapping("/{id}")
public ProductDTO updateProduct(
@PathVariable Long id,
@Valid @RequestBody UpdateProductRequest request) {
Product product = productService.findById(id)
.orElseThrow(() -> new ResourceNotFoundException("Product", "id", id));
mapper.updateEntity(request, product);
Product updatedProduct = productService.save(product);
return mapper.toDTO(updatedProduct);
}
}Implementing Global Exception Handling
A critical aspect of production applications is consistent error handling across all endpoints:
@RestControllerAdvice
@Slf4j
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(ResourceNotFoundException.class)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND)
public ErrorResponse handleResourceNotFoundException(
ResourceNotFoundException ex, WebRequest request) {
log.error("Resource not found: {}", ex.getMessage());
return ErrorResponse.builder()
.timestamp(LocalDateTime.now())
.status(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND.value())
.error("Resource Not Found")
.message(ex.getMessage())
.path(request.getDescription(false))
.build();
}
@ExceptionHandler(MethodArgumentNotValidException.class)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST)
public ErrorResponse handleValidationExceptions(
MethodArgumentNotValidException ex) {
Map<String, String> errors = new HashMap<>();
ex.getBindingResult().getAllErrors().forEach((error) -> {
String fieldName = ((FieldError) error).getField();
String errorMessage = error.getDefaultMessage();
errors.put(fieldName, errorMessage);
});
return ErrorResponse.builder()
.timestamp(LocalDateTime.now())
.status(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value())
.error("Validation Failed")
.message("Invalid input parameters")
.validationErrors(errors)
.build();
}
@ExceptionHandler(DataIntegrityViolationException.class)
@ResponseStatus(HttpStatus.CONFLICT)
public ErrorResponse handleDataIntegrityViolation(
DataIntegrityViolationException ex) {
String message = "Database constraint violation";
if (ex.getCause() instanceof ConstraintViolationException) {
ConstraintViolationException constraintEx =
(ConstraintViolationException) ex.getCause();
if (constraintEx.getConstraintName() != null) {
message = "Constraint violation: " + constraintEx.getConstraintName();
}
}
return ErrorResponse.builder()
.timestamp(LocalDateTime.now())
.status(HttpStatus.CONFLICT.value())
.error("Data Integrity Violation")
.message(message)
.build();
}
}Advanced Configuration Management
Spring Boot's configuration management goes beyond simple property files. Here's how to implement a robust configuration strategy:
@Configuration
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "app")
@Validated
public class ApplicationProperties {
@NotNull
private Security security = new Security();
@NotNull
private Cache cache = new Cache();
@Valid
private List<ExternalService> externalServices = new ArrayList<>();
@Getter
@Setter
public static class Security {
@NotBlank
private String jwtSecret;
@DurationMin(minutes = 5)
private Duration tokenValidity = Duration.ofHours(24);
private boolean enableCsrf = true;
}
@Getter
@Setter
public static class Cache {
private boolean enabled = true;
@DurationMin(seconds = 60)
private Duration ttl = Duration.ofMinutes(10);
private int maxSize = 1000;
}
@Getter
@Setter
public static class ExternalService {
@NotBlank
private String name;
@NotBlank
@URL
private String url;
@DurationMin(millis = 100)
private Duration timeout = Duration.ofSeconds(30);
private RetryConfig retry = new RetryConfig();
}
}Implementing Resilience Patterns
Modern microservices must be resilient to failures. Spring Boot integrates beautifully with resilience libraries:
@Component
@Slf4j
public class ExternalServiceClient {
private final RestTemplate restTemplate;
private final CircuitBreaker circuitBreaker;
private final Retry retry;
public ExternalServiceClient(RestTemplate restTemplate,
CircuitBreakerFactory circuitBreakerFactory,
RetryRegistry retryRegistry) {
this.restTemplate = restTemplate;
this.circuitBreaker = circuitBreakerFactory.create("external-service");
this.retry = retryRegistry.retry("external-service");
}
public Optional<ExternalData> fetchData(String id) {
return circuitBreaker.run(
() -> retry.executeSupplier(() -> {
log.debug("Fetching data for id: {}", id);
ResponseEntity<ExternalData> response = restTemplate.getForEntity(
"/api/data/{id}",
ExternalData.class,
id
);
return Optional.ofNullable(response.getBody());
}),
throwable -> {
log.error("Failed to fetch data for id: {}, falling back", id, throwable);
return Optional.empty();
}
);
}
}
@Configuration
public class ResilienceConfig {
@Bean
public CircuitBreakerFactory circuitBreakerFactory() {
CircuitBreakerConfig circuitBreakerConfig = CircuitBreakerConfig.custom()
.failureRateThreshold(50)
.waitDurationInOpenState(Duration.ofSeconds(30))
.slidingWindowSize(10)
.permittedNumberOfCallsInHalfOpenState(3)
.slowCallRateThreshold(50)
.slowCallDurationThreshold(Duration.ofSeconds(2))
.build();
CircuitBreakerRegistry registry = CircuitBreakerRegistry.of(circuitBreakerConfig);
return new Resilience4JCircuitBreakerFactory(registry, null);
}
@Bean
public RetryRegistry retryRegistry() {
RetryConfig retryConfig = RetryConfig.custom()
.maxAttempts(3)
.waitDuration(Duration.ofMillis(500))
.retryExceptions(RestClientException.class)
.ignoreExceptions(IllegalArgumentException.class)
.build();
return RetryRegistry.of(retryConfig);
}
}Database Migration and Versioning
Managing database schema evolution is crucial. Spring Boot integrates seamlessly with Flyway:
-- V1__Create_product_table.sql
CREATE TABLE product (
id BIGSERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
name VARCHAR(255) NOT NULL,
description TEXT,
price DECIMAL(10, 2) NOT NULL,
category VARCHAR(100),
stock_quantity INTEGER NOT NULL DEFAULT 0,
created_at TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
updated_at TIMESTAMP NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP,
version BIGINT NOT NULL DEFAULT 0
);
CREATE INDEX idx_product_category ON product(category);
CREATE INDEX idx_product_price ON product(price);
-- V2__Add_product_status.sql
ALTER TABLE product
ADD COLUMN status VARCHAR(50) NOT NULL DEFAULT 'ACTIVE';
CREATE INDEX idx_product_status ON product(status);Monitoring and Observability
Spring Boot Actuator provides production-ready monitoring features:
@Component
@Endpoint(id = "custom-health")
public class CustomHealthEndpoint {
private final DataSource dataSource;
private final RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory;
@ReadOperation
public Health health() {
return Health.up()
.withDetail("database", checkDatabase())
.withDetail("redis", checkRedis())
.withDetail("timestamp", LocalDateTime.now())
.build();
}
private String checkDatabase() {
try (Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection()) {
return connection.isValid(1) ? "UP" : "DOWN";
} catch (SQLException e) {
return "DOWN: " + e.getMessage();
}
}
private String checkRedis() {
try {
redisConnectionFactory.getConnection().ping();
return "UP";
} catch (Exception e) {
return "DOWN: " + e.getMessage();
}
}
}
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/actuator/metrics")
public class CustomMetricsController {
private final MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
Gauge.builder("business.active_users", this::getActiveUserCount)
.description("Number of active users in the system")
.register(meterRegistry);
}
private double getActiveUserCount() {
// Implementation to get active user count
return userService.getActiveUserCount();
}
}Security Configuration
Implementing comprehensive security with Spring Security:
@Configuration
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(prePostEnabled = true)
public class SecurityConfig {
@Bean
public SecurityFilterChain filterChain(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.cors().and()
.csrf().disable()
.sessionManagement()
.sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS)
.and()
.authorizeRequests()
.antMatchers("/api/auth/**", "/actuator/health").permitAll()
.antMatchers(HttpMethod.GET, "/api/products/**").permitAll()
.antMatchers("/api/admin/**").hasRole("ADMIN")
.anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.addFilterBefore(jwtAuthenticationFilter(), UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter.class)
.exceptionHandling()
.authenticationEntryPoint(unauthorizedHandler);
return http.build();
}
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder(12);
}
}Resources for Spring Boot Development
To accelerate your Spring Boot development journey and build enterprise-grade applications, here are essential resources:
IDE and Development Tools
- IntelliJ IDEA Ultimate - The most powerful Java IDE with excellent Spring Boot support
- Spring Tools Suite - Eclipse-based IDE optimized for Spring development
- JRebel - Hot reload tool that saves development time by eliminating restarts
Cloud Hosting and Deployment
- AWS Elastic Beanstalk - Easy deployment platform for Spring Boot applications
- Heroku - Platform-as-a-Service with excellent Spring Boot buildpack support
- Google Cloud Platform - Enterprise cloud platform with Spring Boot integration
Monitoring and APM Solutions
- New Relic Java Agent - Deep application performance monitoring for Spring Boot
- Dynatrace - AI-powered full stack monitoring solution
- AppDynamics - Business and application performance monitoring
Learning Resources
- Spring Boot in Action - Comprehensive book on Spring Boot best practices
- Udemy Spring Boot Courses - Video courses from beginner to advanced
Essential Libraries and Tools
- MapStruct - Code generator for type-safe bean mappings
- Lombok - Reduce boilerplate code with annotations
- Testcontainers - Integration testing with Docker containers
- Spring Cloud - Microservices patterns and distributed systems
Database and Caching Solutions
- PostgreSQL on Amazon RDS - Managed PostgreSQL for Spring Boot applications
- Redis Enterprise - High-performance caching solution
- MongoDB Atlas - Fully managed NoSQL database service
Spring Boot continues to evolve as the framework of choice for building modern Java applications. By mastering these advanced concepts and leveraging the right tools, you'll be well-equipped to build scalable, maintainable microservices that can handle the demands of production environments.
Gopi Gorantala Newsletter
Join the newsletter to receive the latest updates in your inbox.